The Institut für angewandte numerische Wissenschaft e.V. (Institute for Applied Numerical Science, IANW) is a nonprofit research institute engaging in the development and application of numerical methods. Several technologies ranging from artificial intelligence via blockchain up to computational fluid dynamics are based on numerical methods, making these essential for both economy and science.
The goal of the IANW is to combine and apply recent results from computer science, physics, and mathematics. Thereby, new numerical methods are developed and applied in practice. Another focus is the development and application of novel tools for simple and efficient usage of modern heterogeneous hardware systems.
Numerical Methods
Many models in physics, science, and engineering are very complex and necessitate numerical methods to approximate solutions. These include for example the computation of air flows, the analysis of inflammation processes in the human body, and the simulation of defibrillators.
To satisfy the increasing demands, numerical methods have to be improved continuously. For balance laws in continuum physics and phenomena such as turbulence, high order methods play an important role. To be able to cope with current and future challenges, their robustness and stability have to be ensured.
In this context, plasma physics is in the current research focus of the IANW. In particular, the simulation of phenomena in the magnetosphere of the earth and the influence of inhomogeneities are of interest.

Machine Learning
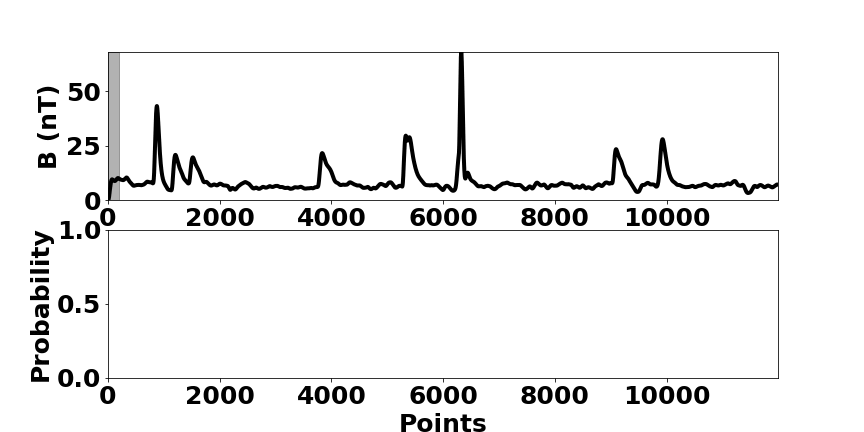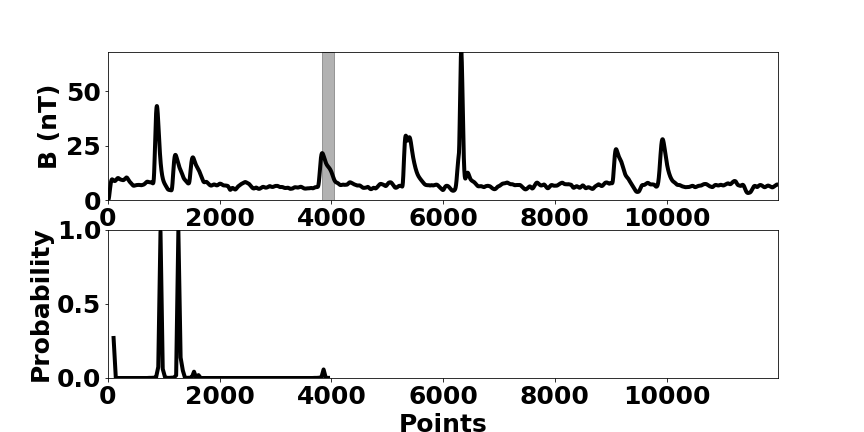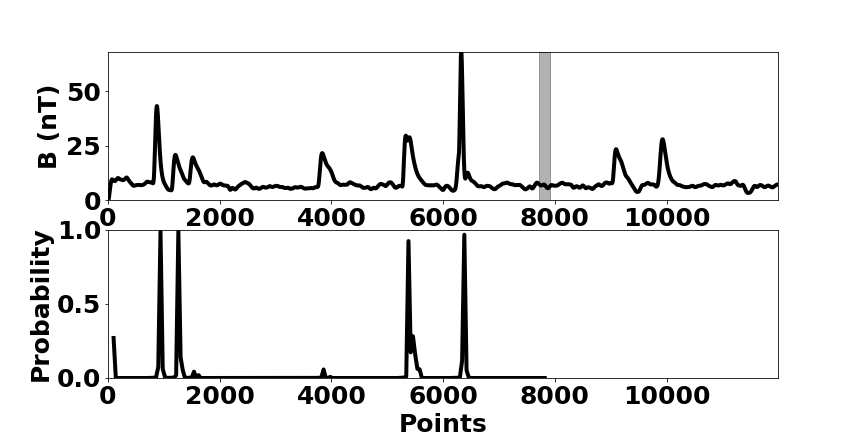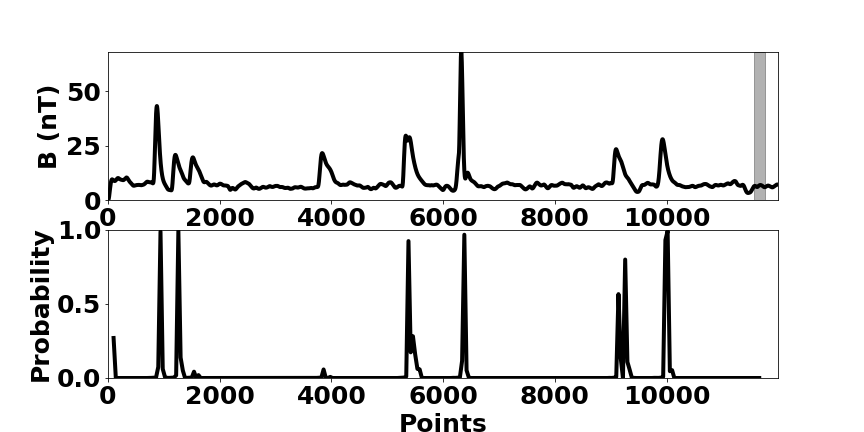
Because of the ever-increasing amount of data, machine learning has gained more and more in prominence over recent years. Facilitated by the immense increase in computational power over the last years, mainly in the form of GPUs, it was possible to implement efficient algorithms, e.g. in the area of image recognition and natural language processing.
Motivated by this recent progress, the IANW researches the application and development of methods for automated data analysis in the context of large scale physics projects. Thereby, the implementation of these methods on various hardware is an integral part. One main focus is the automated recognition of patterns in time series for large scale statistical studies or process monitoring.
High Performance Computing
The performance increase of modern hardware systems is based on massive parallelization. Numerous concepts and software implementations are available to make use of these features, which makes choosing the right approach challenging. Therefore, the IANW is developing tools to help with the implementation and application of parallel algorithms.
Machine learning and highly complex simulations for physics and engineering applications are based on executing similar operations on large datasets. The IANW is developing corresponding software to measure and optimize runtime and energy efficiency of different algorithms depending on the hardware platform.

